Servo Motor Glossary of Terms
Encoder
Encoder
The encoder is a sensor that notifies the driver of the speed and position of the motor. The encoders (position detectors) used in the servo motor can be structurally classified as "incremental encoders" and "absolute encoders". Oriental Motor uses a 20-bit absolute encoder for our servo motors NX series for low vibration at low speed range.
Absolute Encoder
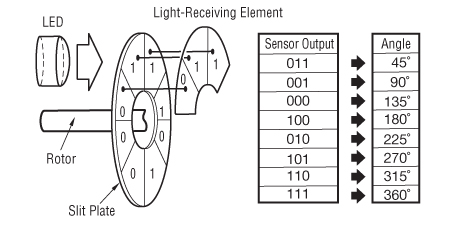
Capable of detecting absolute position within one rotation of the servo motor, the absolute encoder outputs the absolute position of the rotation angle. Ordinarily, multiple rotation information is transmitted to the servo amp when the power source is turned on, and that information is then outputted to the current position data.
Incremental Encoder
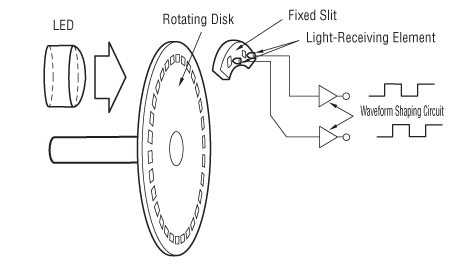
Capable of detecting the rotation, speed and rotation direction of the servo motor, the incremental encoder outputs the pulse with respect to the change portion of the rotation angle. Ordinarily, the detection waveform output is without modification, and therefore the current position is lost when the power is off.
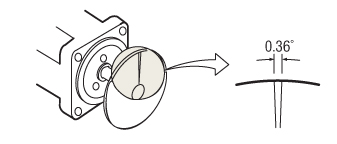
Resolution
The angle is shown for the motor rotation with one pulse. The resolution determines the positioning accuracy of the motor. For example, if the resolution is 1000 p/rev, one rotation of the motor (360°) can be divided into 1000 parts.
Speed Control and Position Control
The NX series speed and positioning control commands are carried out by inputting a pulse signal the same as with a stepping motor. In the relationship of the pulse speed and position,
- the rotation angle (position) is proportional to the number of pulses, and
- the speed is proportional to the pulse frequency.
Additionally, torque control and tension control are carried out.
Max. Input Pulse Frequency
This is the maximum pulse frequency (speed) that can be inputted to the driver. The maximum rotation speed of the motor is limited by the driver. If a frequency exceeding that speed is input to the driver, the motor cannot follow and an alarm is outputted.
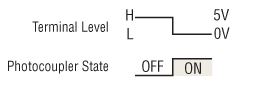
Photocoupler "ON" and "OFF"
Input (output) "ON" indicates that the current is sent into the photocoupler (transistor) inside the driver. Input (output) "OFF" indicates that the current is not sent into the photocoupler (transistor) inside the driver.
Pulse Speed
For the pulse input type, the motor speed is proportional to the input pulse speed (pulse frequency).

Deviation Counter
The deviation counter has the function of counting the deviation of the input pulse and the feedback pulse in the driver. When a pulse is input to the driver, the counter adds the pulse (accumulated pulse), and when the motor rotates, a positioning control is carried out so that the accumulated pulse in the counter is subtracted by the feedback signal and the accumulated pulse goes to zero.
Hunting
During a standstill, the output shaft of the servo motor may vibrate slightly. This phenomenon is called hunting.
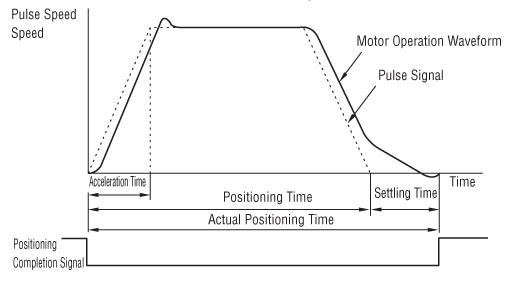
Settling Time
A delay occur between the position command of the pulse input and the actual motor operation. The time difference occurring at a motor standstill is referred to as the settling time.
Gain Adjustment
Gain adjustment is carried out to optimize the control according to the load.
Accumulated Pulse
The difference of the command pulse input to the servo driver, and the feedback pulse output according to the motor rotation from the encoder that is built in the AC servo motor is referred to as the accumulated pulse.
